boolean_dialog · continue_dialog · string_dialog
Dialog Boxes
- boolean_dialog()
Syntax:
n.boolean_dialog("label", ["accept", "cancel"])
- Description:
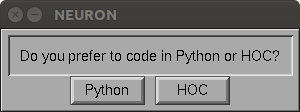
Pops up a dialog window at the center of the screen and blocks everything until dealt with. Returns 1 or 0.
Example:
from neuron import n, gui if n.boolean_dialog('Do you prefer to code in Python or HOC?', 'Python', 'HOC'): print('You prefer Python!') else: print('You prefer HOC!')
- Syntax:
boolean_dialog("label", ["accept", "cancel"])- Description:
Pops up a dialog window at the center of the screen and blocks everything until dealt with. Returns 1 or 0.
See also
- continue_dialog()
Syntax:
n.continue_dialog("message")
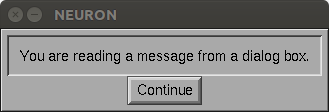
- Description:
Provides information to the user. Like
boolean_dialog(), blocks everything until dealt with.
Example:
from neuron import n, gui n.continue_dialog("You are reading a message from a dialog box.")
- Syntax:
continue_dialog("label")- Description:
Provides info to the user. Like
boolean_dialog(), blocks everything until dealt with.
- string_dialog()
- Syntax:
n.string_dialog("message", strref)
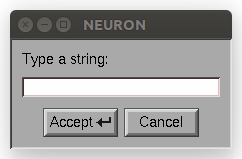
- Description:
Prompts the user to enter a string. The initial value of strref is used as the default value. If canceled, returns 0 and strref remains unchanged. Otherwise, returns 1 and strref is replaced with the entered text. Like
boolean_dialog(), blocks everything until dealt with.
Example:
from neuron import n, gui my_str = n.ref('') if n.string_dialog('Type a string:', my_str): print(f'You typed: {my_str[0]}') else: print('You canceled')
- Syntax:
string_dialog("label", strdef)- Description:
Returns 0 if canceled and strdef remains unchanged. Like
boolean_dialog(), blocks everything until dealt with.